Using Google Maps
If you want to conveniently convey details of places, directions and routes to the end-user, Google Maps is an essential part of your app. Luckily, there is an official google_maps_flutter available for Flutter.
- Creating a GCP project
-
Go to the GCP console
-
Go to the Project Selection dialog box and click New Project.
-
Enter a name for your project and click Create.
- Enabling APIs
-
Go to APIs & Services from the left menu and select Library.
-
Now, search for Maps and enable Maps SDK for both platforms.
-
You will also need the Directions API while drawing the routes. So enable that as well.
- Generating an API key
-
Go to APIs & Services from the left menu and select Credentials.
-
Click CREATE CREDENTIALS and select API key.
- Set up the Flutter project
-
Create a new Flutter project.
-
Open the project using your favorite IDE. For opening with VS Code:
-
Add the google_maps_flutter plugin to the pubspec.yaml file:
- Integrating the Google Maps Widget
-
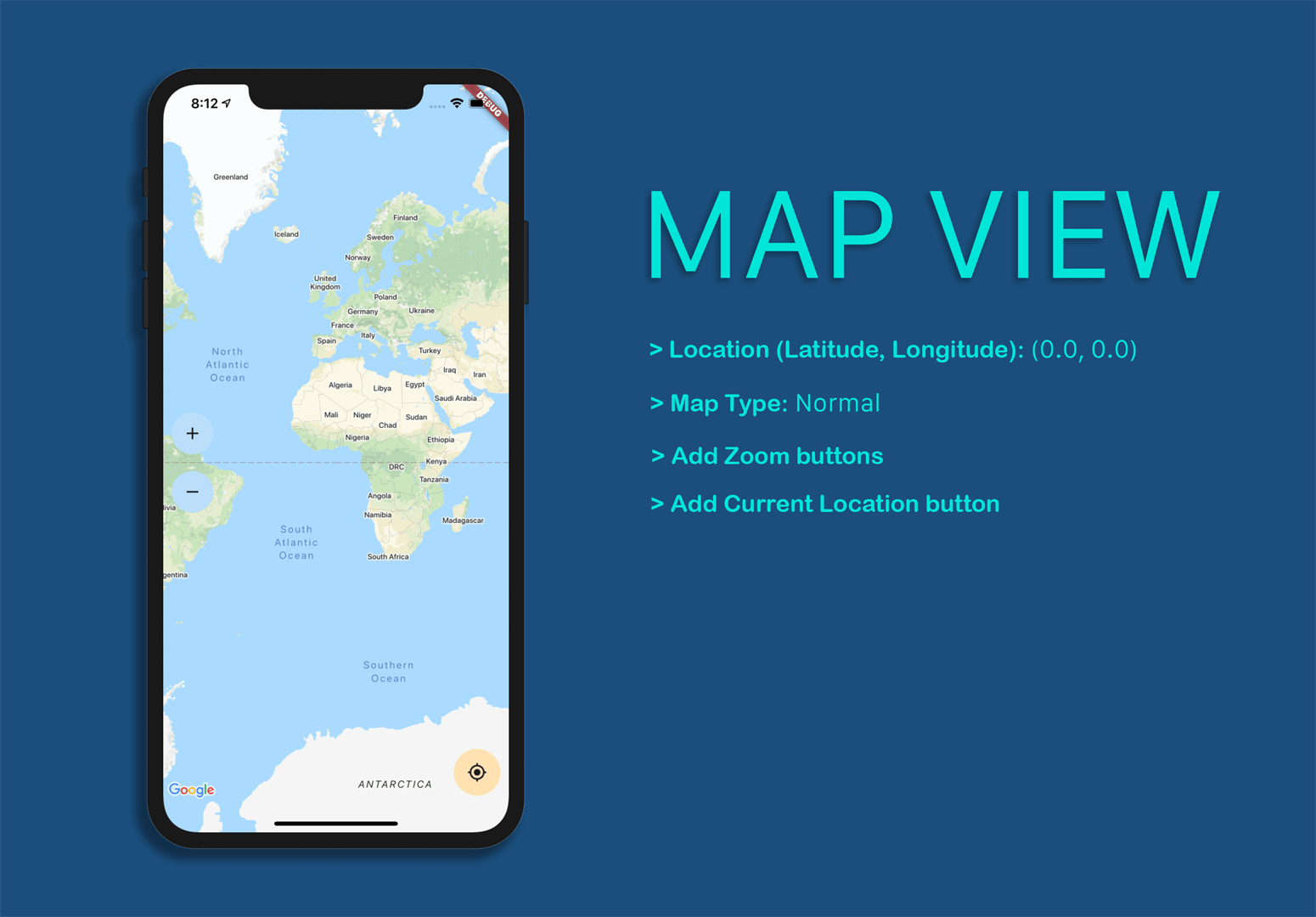
initialCameraPosition : This is a required parameter that is used for loading the map view on initial start-up.
-
myLocationEnabled: For showing your current location on the map with a blue dot.
-
myLocationButtonEnabled: This button is used to bring the user location to the center of the camera view.
-
mapType: For specifying the displayed map type (normal, satellite, hybrid or terrain).
-
zoomGesturesEnabled: Whether the map view should respond to zoom gestures.
-
zoomControlsEnabled: Whether to show zoom controls (only applicable for Android).
-
onMapCreated: Callback for when the map is ready to use.
- Fetching current location
-
Define a variable to store the retrieved current location:
-
Get the current location of the user:
-
Add this method to the initState to fetch the user’s current location as soon as the app launches, and to move the camera to the detected location
-
Also pass the latitude and longitude to the onTap method of the custom button for fetching the current location.
- Placing Markers
-
First of all, define a variable for storing the markers:
-
Create the markers:
-
Add the markers:
-
Display the markers on the map:
You will need a GCP project to get access to the Google Maps API and generate an API key.
To create a new GCP project, follow the steps below:
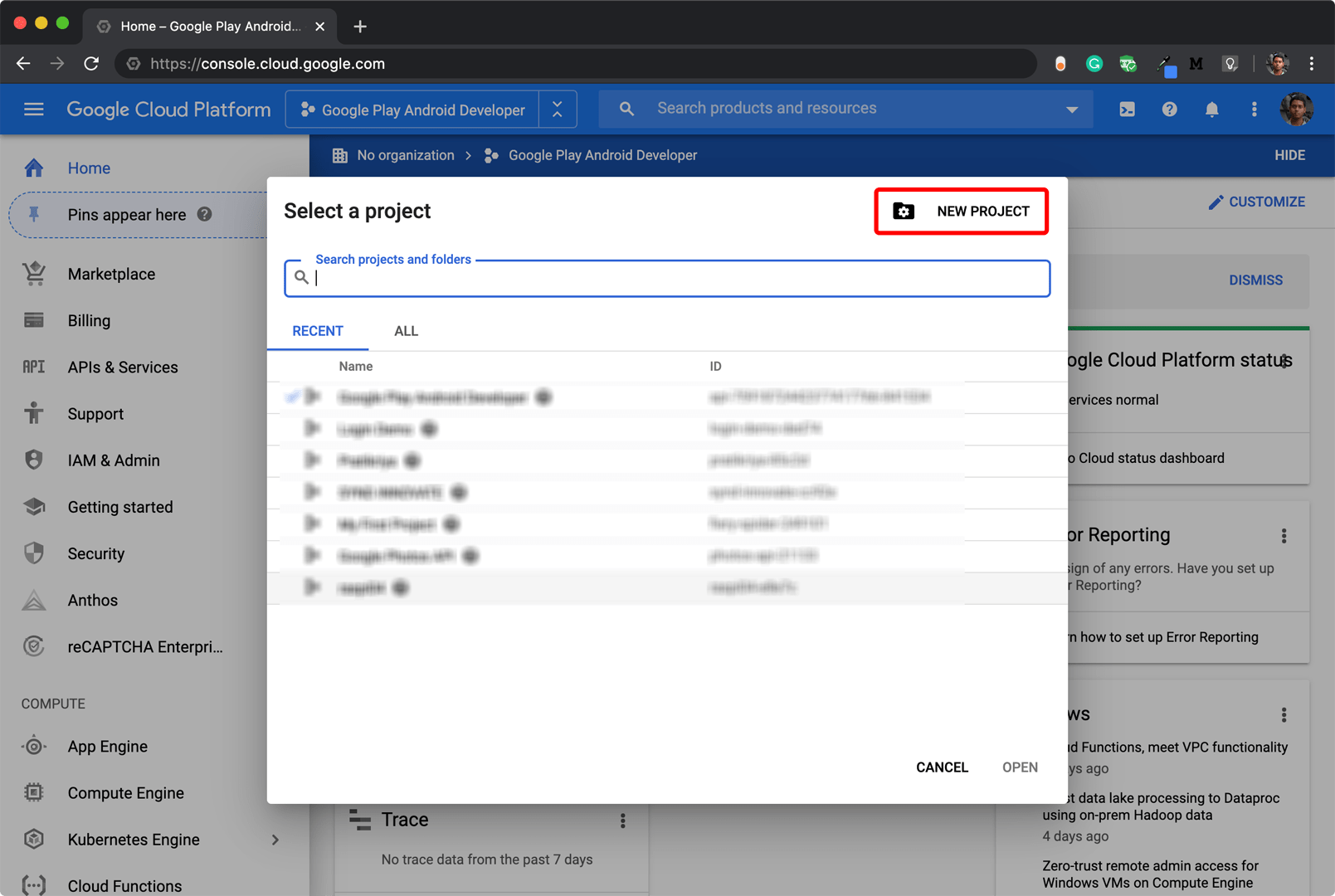
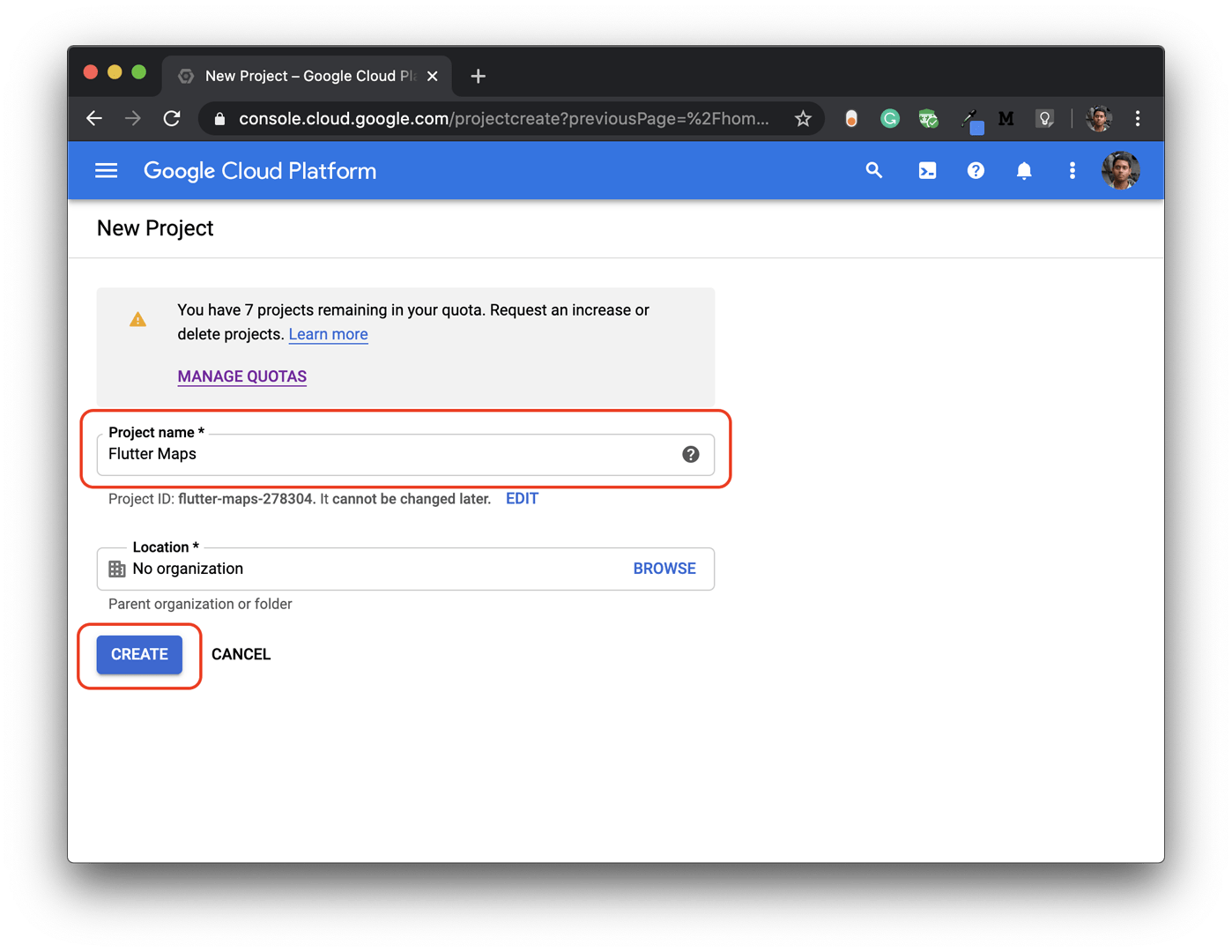
This will create a new GCP Project.
In order to use Google Maps in your app, you will need to enable Maps SDK for both platforms.
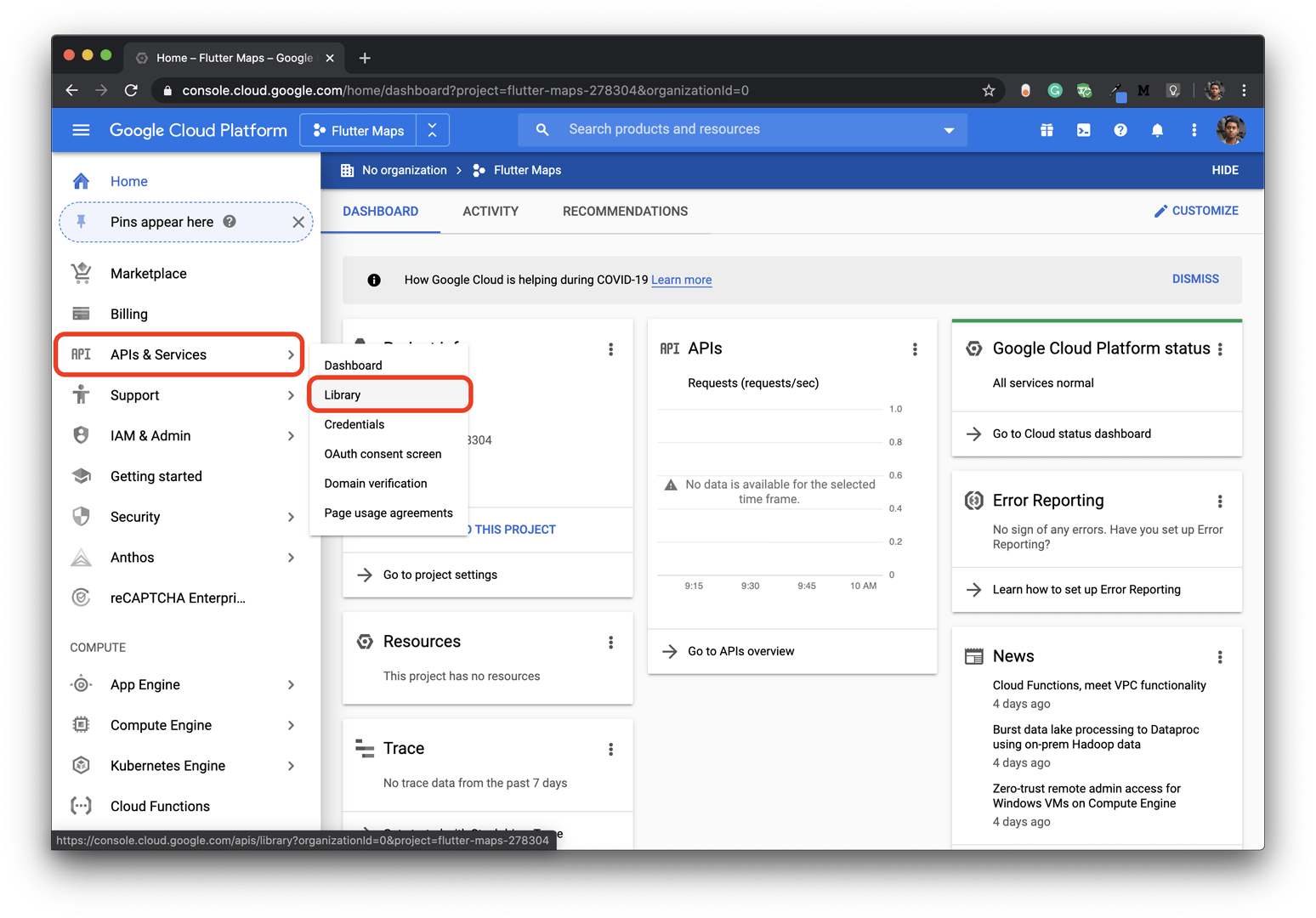
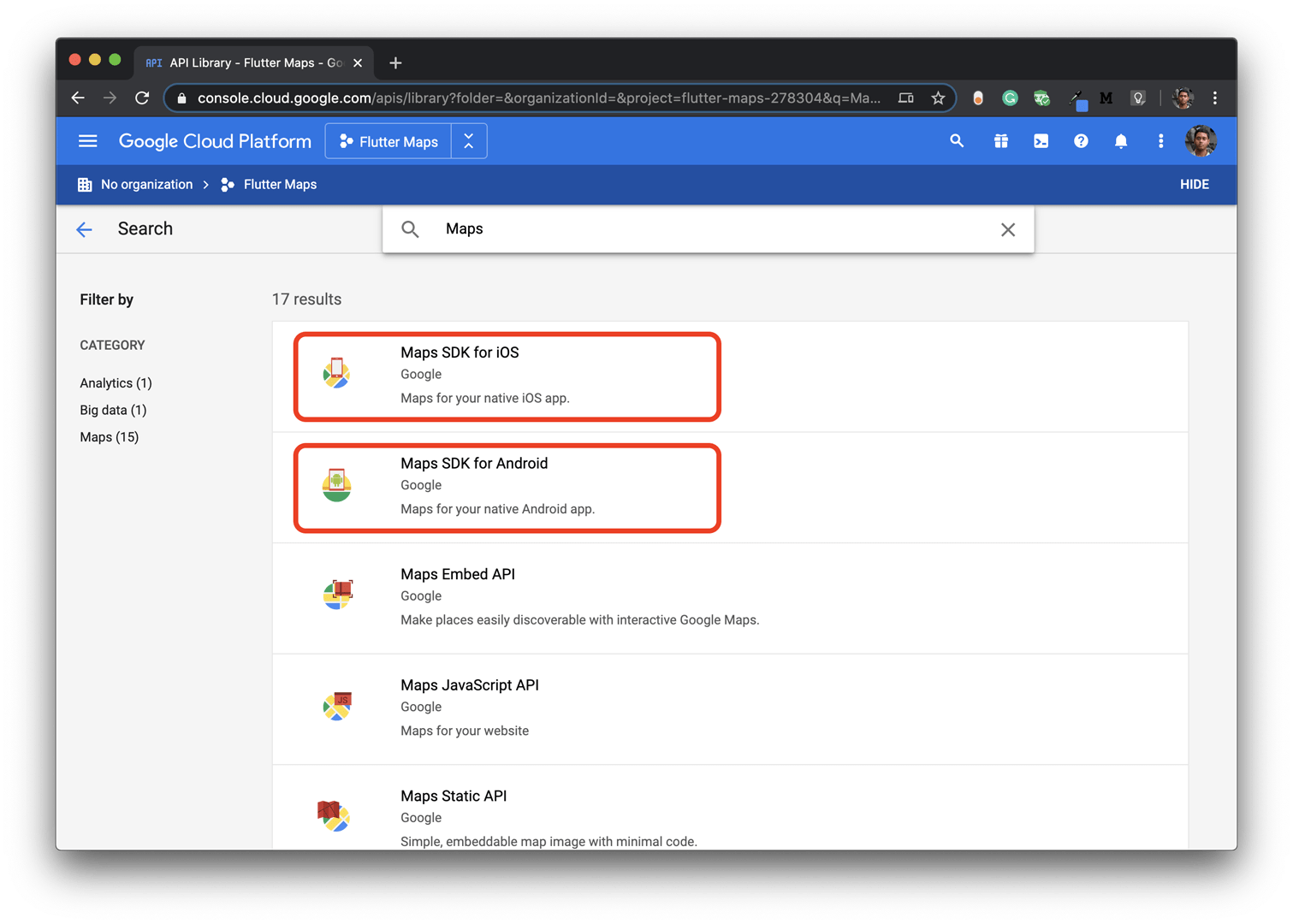
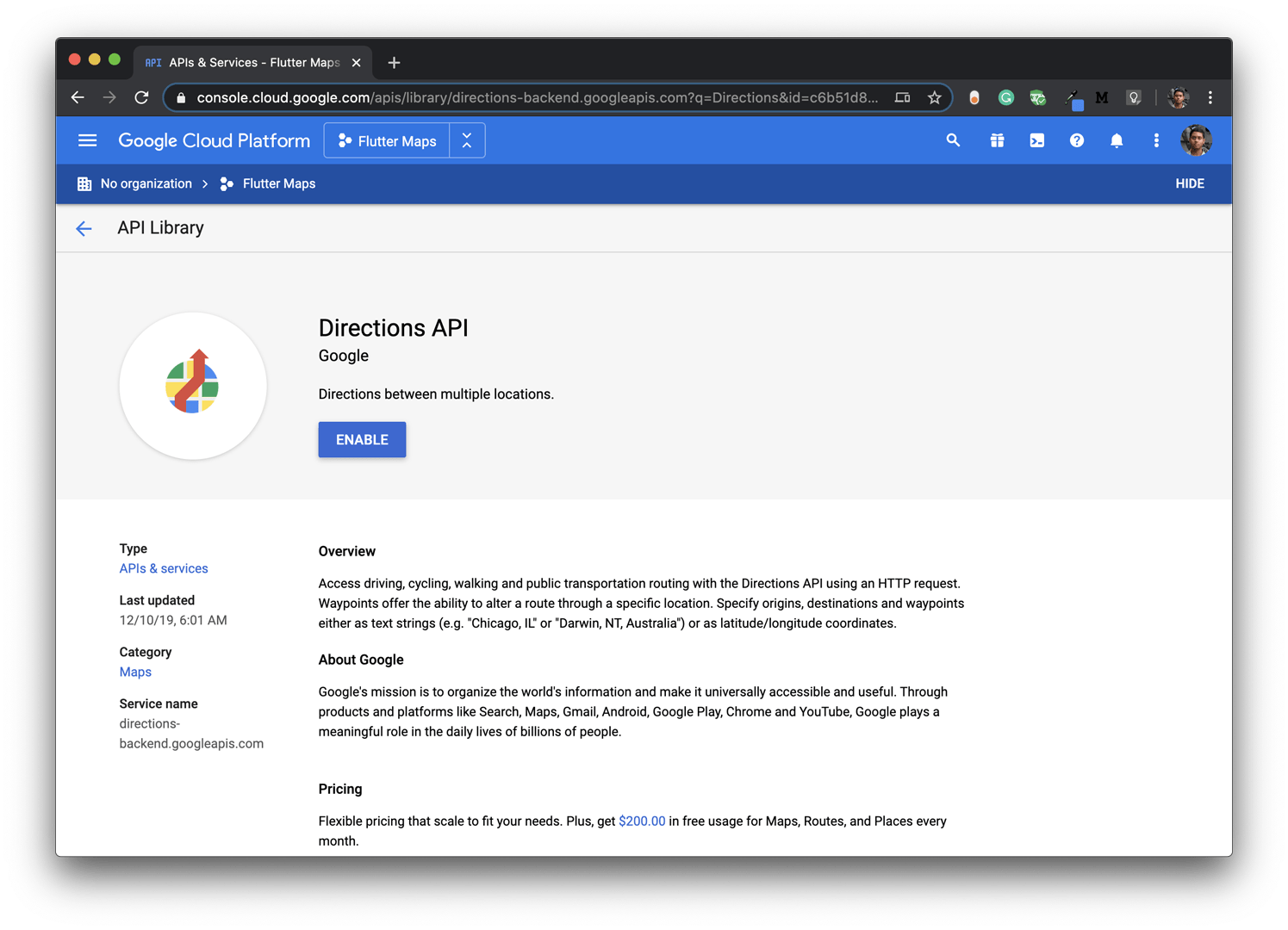
You will need an API key for integrating Google Maps with your app.
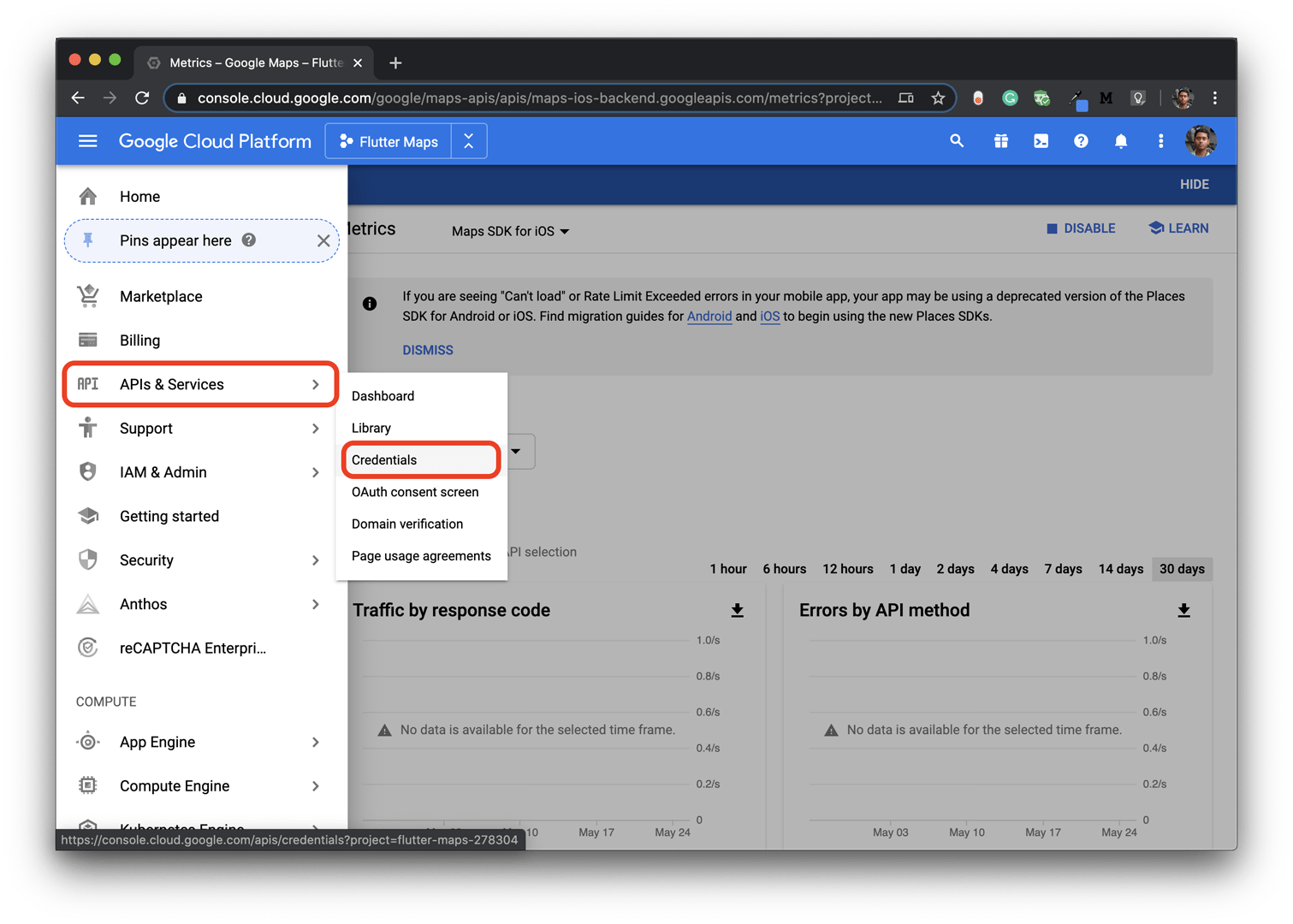
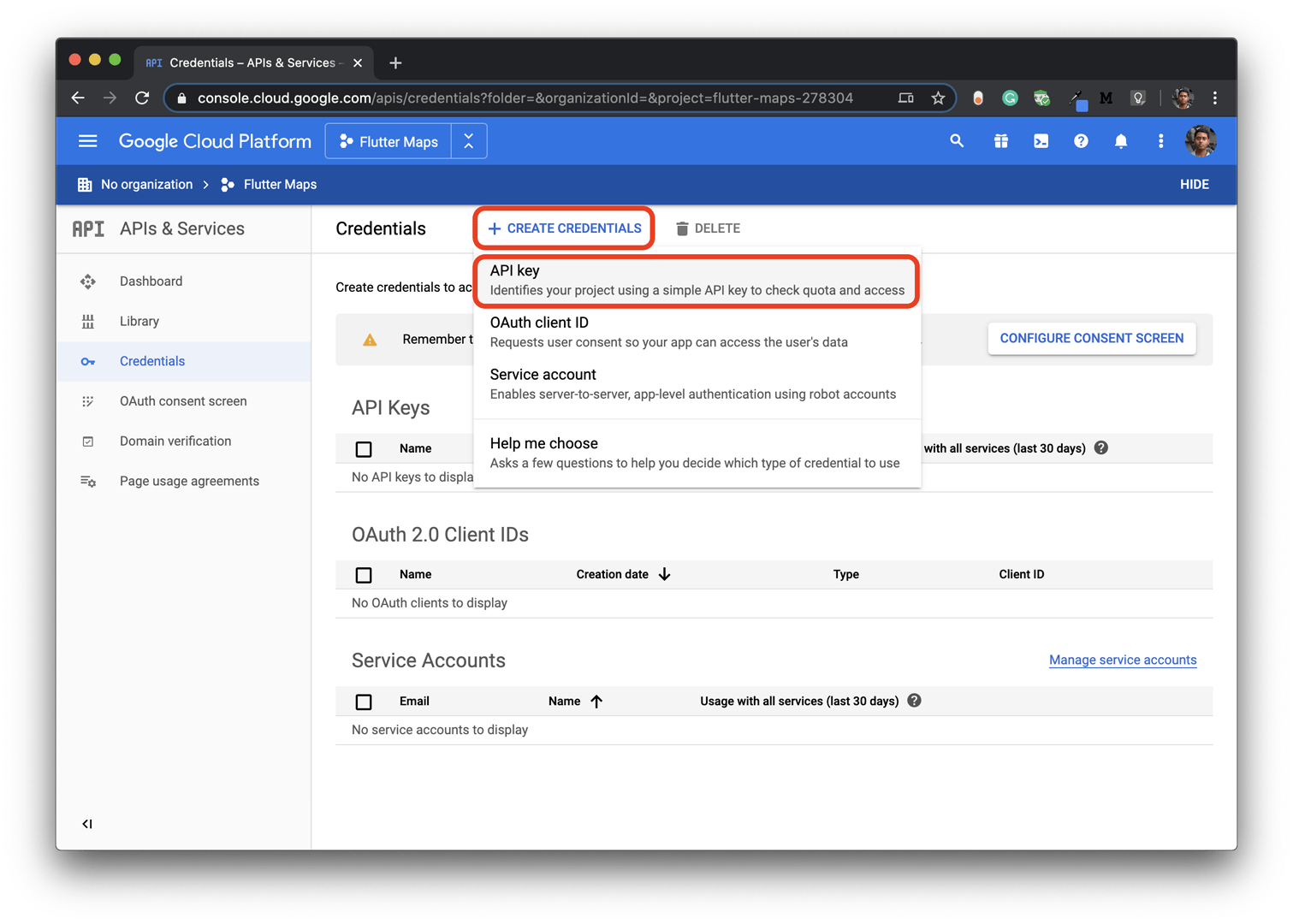
This will generate an API key that you will need in the next step.
Android setup
Go to android/app/build.gradle and set the minSdkVersion to 20:
android {
defaultConfig {
minSdkVersion 20
}
}
Navigate to the file android/app/src/main/AndroidManifest.xml and add the following code snippet inside the application tag:
<!-- Add your Google Maps API Key here --><meta-dataandroid:name="com.google.android.geo.API_KEY"
android:value="YOUR KEY HERE"/>
You will also need the location access in the app. Add the following permission in the same file inside the manifest tag:
§ <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION"/>
iOS setup
Navigate to the file ios/Runner/AppDelegate.swift and replace the whole code with the following:
import UIKit
import Flutter
import GoogleMaps
@UIApplicationMain
@objc class AppDelegate: FlutterAppDelegate {
override func application(
_ application: UIApplication,
didFinishLaunchingWithOptions launchOptions: [UIApplication.LaunchOptionsKey: Any]?
) -> Bool {
//Add your Google Maps API Key here
GMSServices.provideAPIKey("YOUR KEY HERE")
GeneratedPluginRegistrant.register(with: self)
return super.application(application, didFinishLaunchingWithOptions: launchOptions)
}
}
To get the location permission, add the following to the same file:
<key>NSLocationWhenInUseUsageDescription</key>
<string>This app needs access to location when open.</string>
This completes the setup for both platforms in Flutter.
Now you are ready to add the Google Maps widget to your Flutter app.
You can start with the following code:
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
void main() {
runApp(MyApp());
}
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
title: 'Flutter Maps',
theme: ThemeData(
primarySwatch: Colors.blue,
),
home: MapView(),
);
}
}
class MapView extends StatefulWidget {
@override
_MapViewState createState() => _MapViewState();
}
class _MapViewState extends State<MapView> {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
// Determining the screen width & height
var height = MediaQuery.of(context).size.height;
var width = MediaQuery.of(context).size.width;
return Container(
height: height,
width: width,
child: Scaffold(
body: Stack(
children: <Widget>[
// TODO: Add Map View
],
),
),
);
}
}
I have defined the Container height and width to be the size of the screen so that the
Google Maps widget
takes up the entire screen.
I am also using a Stack to keep Google Maps widget in the background and add other
necessary widgets on top
of it.
Now replace the TODO in the above code snippet with the Google Maps widget.
// Import the Google Maps package
import 'package:google_maps_flutter/google_maps_flutter.dart';
// Initial location of the Map view
CameraPosition _initialLocation = CameraPosition(target: LatLng(0.0, 0.0));
// For controlling the view of the Map
late GoogleMapController mapController;
// Replace the "TODO" with this widget
GoogleMap(
initialCameraPosition: _initialLocation,
myLocationEnabled: true,
myLocationButtonEnabled: false,
mapType: MapType.normal,
zoomGesturesEnabled: true,
zoomControlsEnabled: false,
onMapCreated: (GoogleMapController controller) {
mapController = controller;
},
),
Let’s take a look at the parameters defined in the Google Maps widget:
I have set the myLocationButtonEnabled and zoomControlsEnabled parameters
as false because I am going to show you how to define a custom button with the same functionality but with
better control.
mapController would be used to control the camera position of the map view.
By now, the app looks like this:
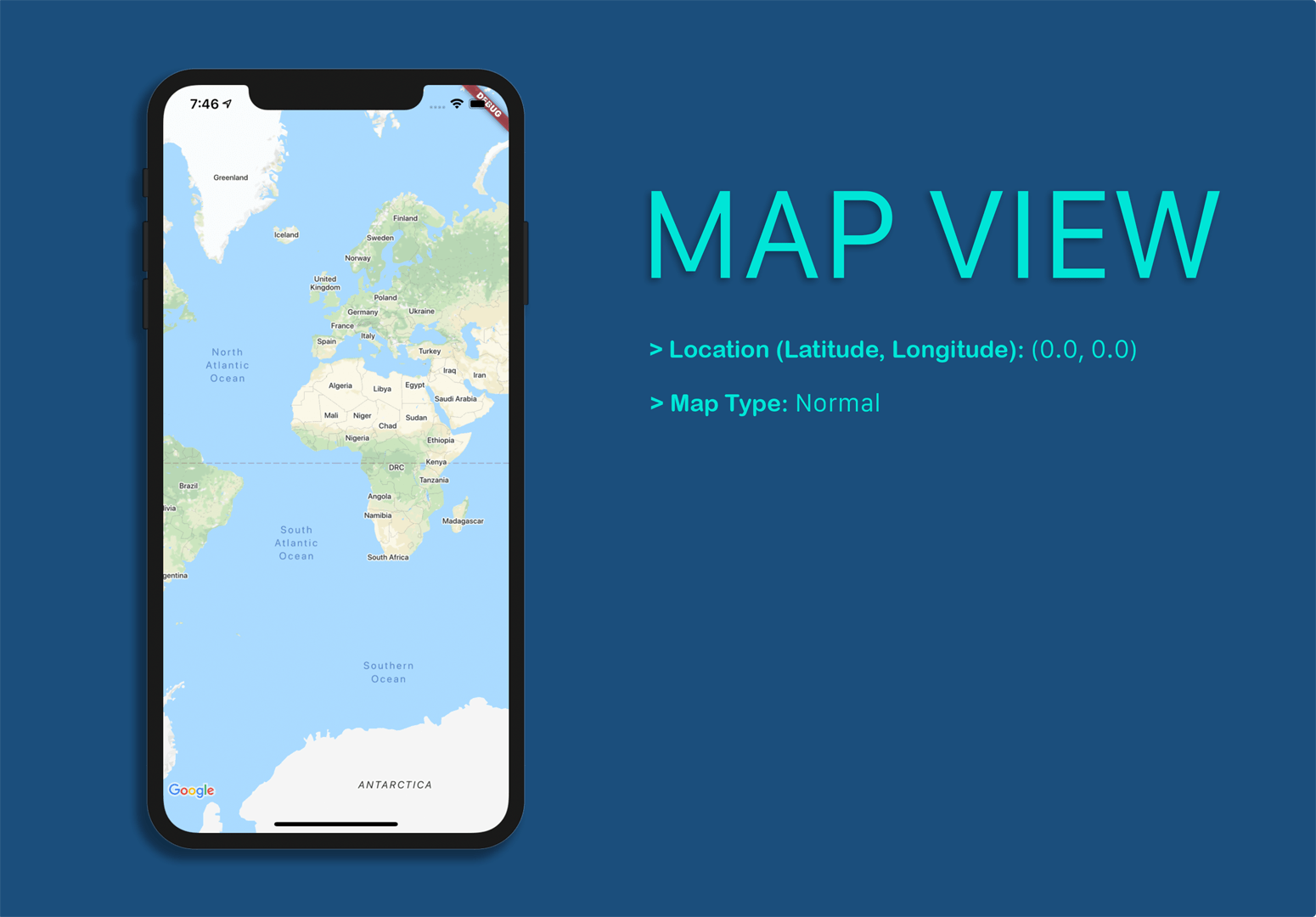
To display the zoom buttons and the current location button you can add them as children to the
Stack widget
and position them accordingly.
The code for designing a button is given below:
// Design for current location button ClipOval( child: Material(color: Colors.orange.shade100,// button color
child: InkWell(splashColor: Colors.orange,// inkwell color
child: SizedBox(width:56,
height:56,
child: Icon(Icons.my_location), ), onTap: () {// TODO: Add the operation to be performed
// on button tap
}, ), ),),Using zoom in the map view
You can use the mapController to zoom in and out on a map.
// Zoom In action
mapController.animateCamera(
CameraUpdate.zoomIn(),
);
// Zoom Out action
mapController.animateCamera(
CameraUpdate.zoomOut(),
);
Move to a new position
You can use the following code snippet to move to a new position:
// Move camera to the specified latitude & longitudemapController.animateCamera( CameraUpdate.newCameraPosition( CameraPosition( target: LatLng(// Will be fetching in the next step
_currentPosition.latitude, _currentPosition.longitude, ),zoom:18.0,
), ),);
Here, I have only specified the target and zoom properties of the CameraPosition widget. There are
two more properties, bearing and tilt that you can use in a similar manner.
In the target property, you have to pass the latitude and longitude of the position you want to
move.
Here, we need the Current Location button to move the camera view to the user’s present location.
Let’s see how to achieve that.
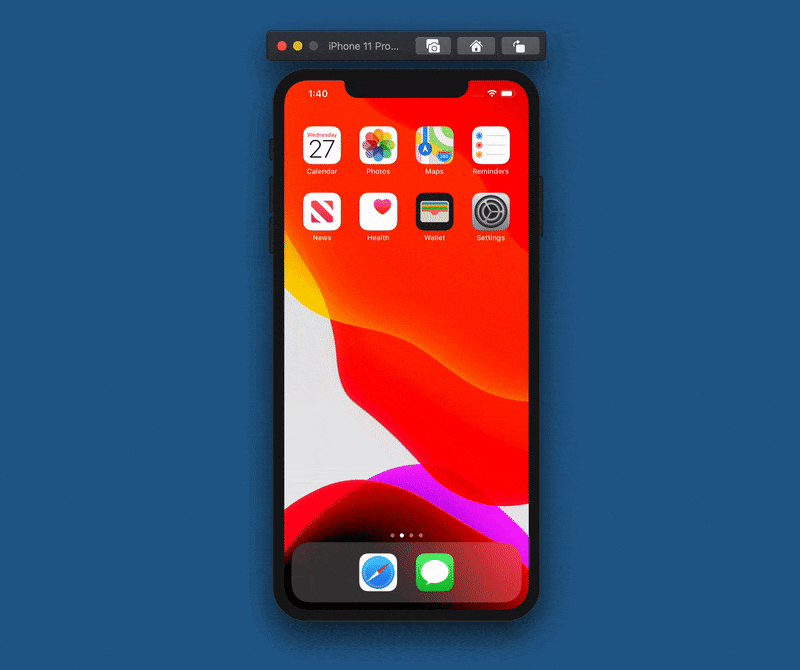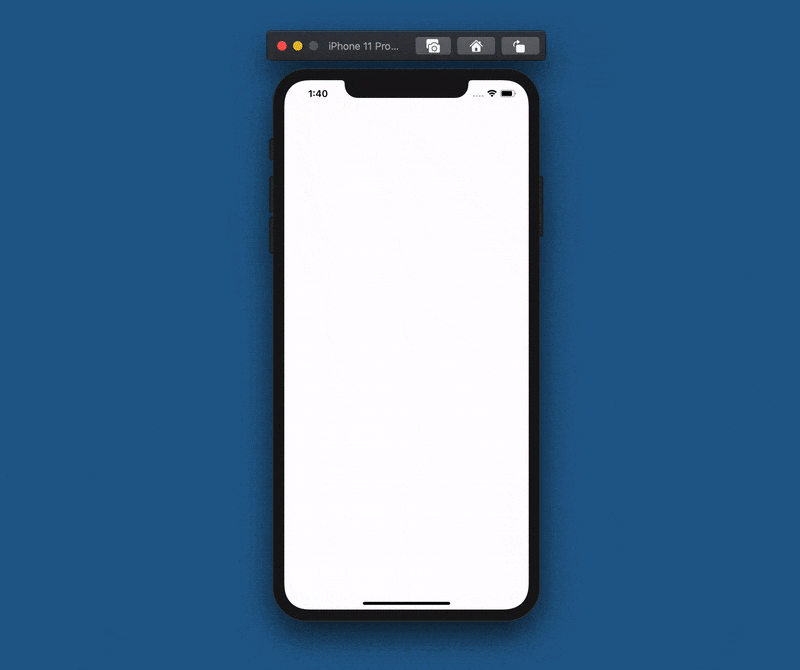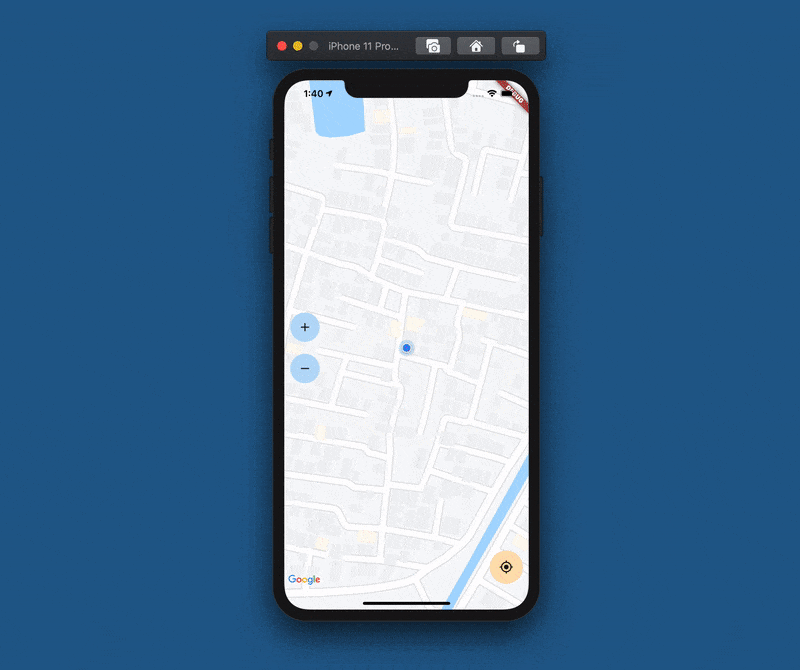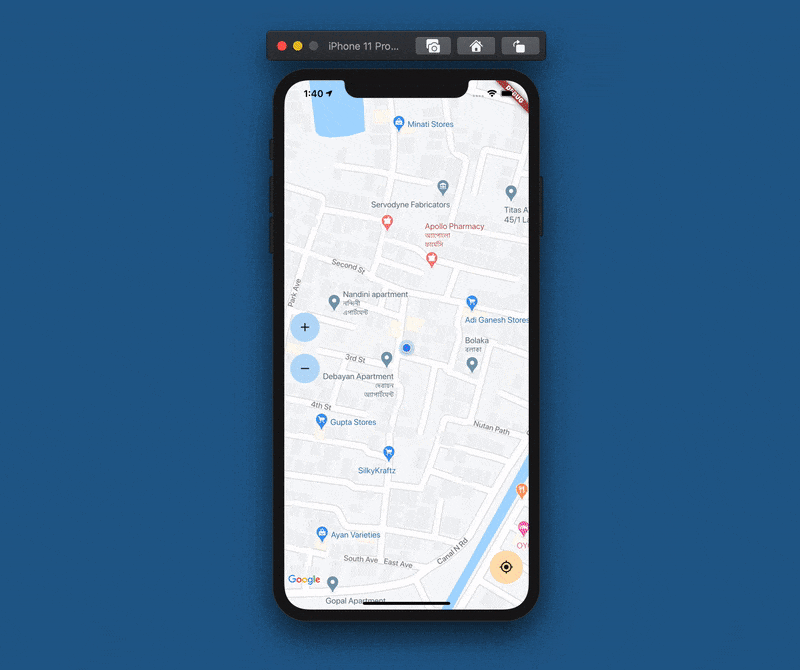
After adding the buttons, the app will look like this:
There is a nice plugin for Flutter called Geolocator
that can help you fetch the user’s
current location.
Add it to your pubspec.yaml file:
geolocator: ^7.0.3Now let’s get started and go through it step-by-step.
// For storing the current positionPosition _currentPosition;// Method for retrieving the current location _getCurrentLocation()async{
awaitGeolocator.getCurrentPosition(desiredAccuracy: LocationAccuracy.high)
.then((Position position)async{
setState(() {// Store the position in the variable
_currentPosition=position;
print('CURRENT POS: $_currentPosition');
// For moving the camera to current location
mapController.animateCamera( CameraUpdate.newCameraPosition( CameraPosition( target: LatLng(position.latitude, position.longitude),zoom:18.0,
), ), ); });await_getAddress();
}).catchError((e) { print(e); });}@override
voidinitState() {
super.initState();
_getCurrentLocation();}After completing these, the camera will automatically move to the detected location as the app launches.
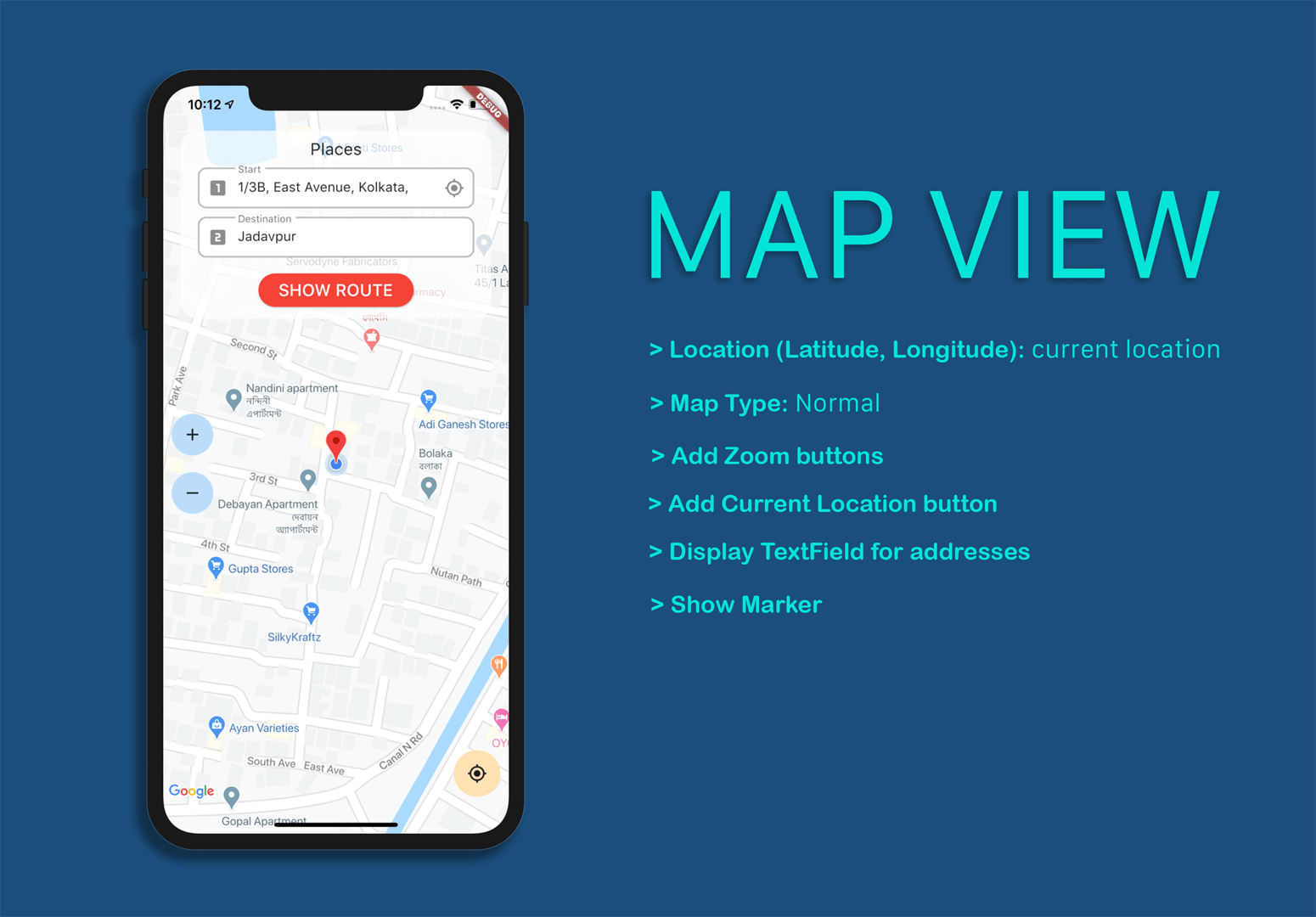
You can use the coordinates retrieved in the previous step to place markers on the map.
§ Set<Marker> markers = {};
String startCoordinatesString = '($startLatitude, $startLongitude)';
String destinationCoordinatesString = '($destinationLatitude, $destinationLongitude)';
// Start Location Marker
Marker startMarker = Marker(
markerId: MarkerId(startCoordinatesString),
position: LatLng(startLatitude, startLongitude),
infoWindow: InfoWindow(
title: 'Start $startCoordinatesString',
snippet: _startAddress,
),
icon: BitmapDescriptor.defaultMarker,
);
// Destination Location Marker
Marker destinationMarker = Marker(
markerId: MarkerId(destinationCoordinatesString),
position: LatLng(destinationLatitude, destinationLongitude),
infoWindow: InfoWindow(
title: 'Destination $destinationCoordinatesString',
snippet: _destinationAddress,
),
icon: BitmapDescriptor.defaultMarker,
);
// Add the markers to the list
markers.add(startMarker);
markers.add(destinationMarker);
// Add the markers property to the widget
GoogleMap(
markers: Set<Marker>.from(markers),
// ...
),
If you run the app now, it will look like this:
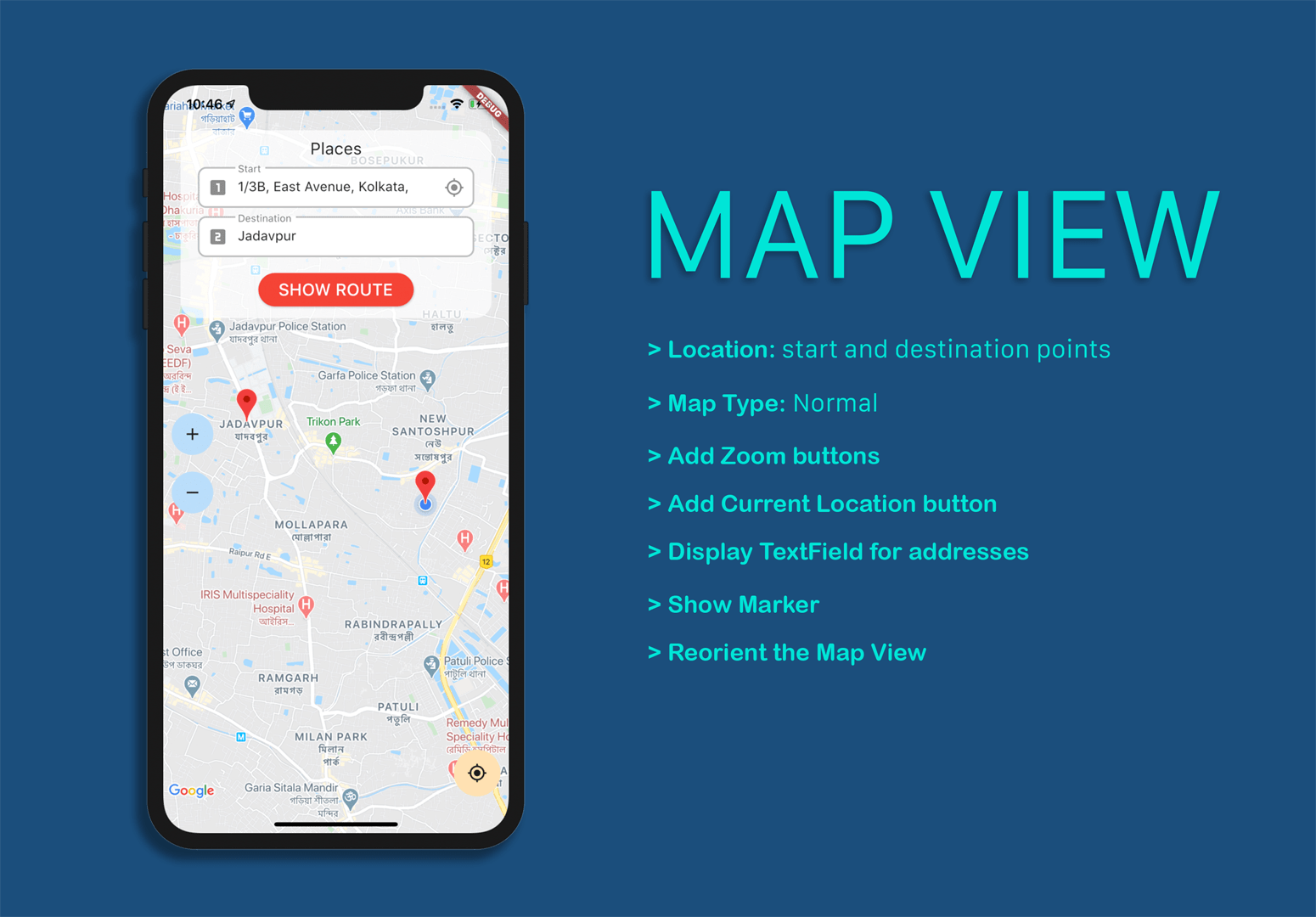
You will notice that only one of the markers is visible, although you placed two of them, one at the
starting point and the other at the destination.
So what’s happening here?
Actually, both markers are added to the map, but only one of them is visible because the other one is
out of the view. If you zoom out a bit, you will notice the other one too.
You can use the following code snippet to reorient the map view to accommodate both markers.
// Calculating to check that the position relative
// to the frame, and pan & zoom the camera accordingly.
double miny = (startLatitude <= destinationLatitude)
? startLatitude
: destinationLatitude;
double minx = (startLongitude <= destinationLongitude)
? startLongitude
: destinationLongitude;
double maxy = (startLatitude <= destinationLatitude)
? destinationLatitude
: startLatitude;
double maxx = (startLongitude <= destinationLongitude)
? destinationLongitude
: startLongitude;
double southWestLatitude = miny;
double southWestLongitude = minx;
double northEastLatitude = maxy;
double northEastLongitude = maxx;
// Accommodate the two locations within the
// camera view of the map
mapController.animateCamera(
CameraUpdate.newLatLngBounds(
LatLngBounds(
northeast: LatLng(northEastLatitude, northEastLongitude),
southwest: LatLng(southWestLatitude, southWestLongitude),
),
100.0,
),
);
For More :
-
Use Geocoding to translate coordinates into a place address and vice versa
-
Draw a route
-
Use Polylines for drawing route between two places
-
Calculate distance of that route
Source : Medium